- Cross section
- Poynting vector
- Microscopy (bright field, dark field, confocal, schieren,...
- Optical force
- Optical torque
- Near field
-
P. C. Chaumet
The Discrete Dipole Approximation : a review
Mathematics 10, 3049 (2022). -
P. C. Chaumet,
P. Bon,
G. Maire,
A. Sentenac and
G. Baffou
Quantitative phase microscopies: accuracy comparison
Light : Science & Applications 13, 288 (2024). -
P. C. Chaumet,
D. Sentenac,
G. Maire,
M. Rasedujjaman,
T. Zhang and
A. Sentenac
IFDDA, an easy-to-use code for simulating the field scattered by 3D inhomogeneous objects in a stratified medium: tutorial
J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 38, 1841 (2021).
Examples of the GUI
The figure below shows how the beam and the object are selected. In the "Illumination Properties" section, the power and the waist (or diameter for the laser beam) are fixed, and then you can choose the beam type from the drop-down menu (linear or circular plane wave, Gaussian wave, antenna, multiple plane waves, etc., or an arbitrary beam). Next, in the "Object Properties" section, you can select the object from the drop-down menu (sphere, cuboid, cylinder, ellipsoid, inhomogeneous sphere, concentric spheres, multiple spheres, etc., or an arbitrary object). By clicking "Props" you can set the characteristics of the object (size), and with "epsilon" and "iso", you can choose the values for permittivity and specify whether it is anisotropic. The discretization option determines the number of layers used to represent the object In the part Study you choose the computation asked: in the present case Microscope for Holographic microscope, and optical force and field inside the object.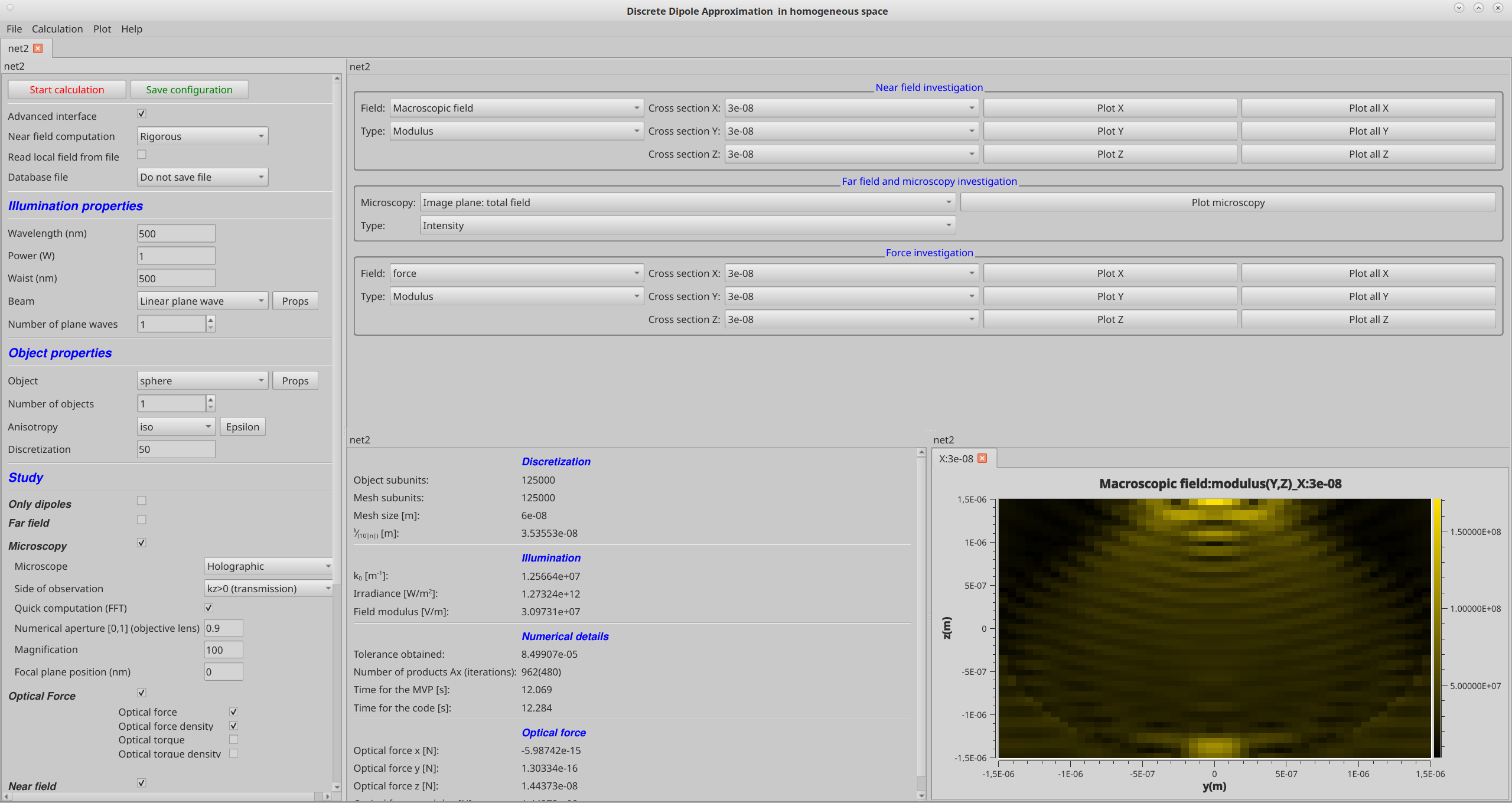
Then we can use matlab (with UI interface) or the graphical interface of the code (right side of the figure) to see the results.
To get more images you can use this link.
IFDDA(M) has been developed by
P. C. Chaumet, A. Sentenac, Aix-Marseille University (France).D. Sentenac, Università di Pisa (Italy).
User Guide.
The reader can find more details on the code with the user guide in English or in French.| IFDDA | IFDDAM | |
| User Guide in English | Userguide | Userguide |
| User Guide in French | Userguide | Userguide |
How to download the code
| IFDDA | IFDDAM | |
| Download the tgz file | IFDDA (Qt6) | IFDDAM (Qt5) |
| Download with gitlab | IFDDA | IFDDAM |
The code use Qt5 for the version 0.x.x et Qt6 for the version 1.x.x
How to install the code
You should uncompressed the file with tar -xvzf cdm-x.x.x.tgz for IFDDA or tar -xvzf cdmsurf-x.x.x.tgz for IFDDAM. A readme or install is given in the tar file. Please read it to install the code on linux system. Note that the code can be installed on windows system (it can be tricky to install FFTW on the windows system, see www.fftw.org/install/windows for details.How to cite the code
-If only the basic functions of the code are used:P. C. Chaumet, D. Sentenac, G. Maire, M. Rasedujjaman, T. Zhang and A. Sentenac
IFDDA, an easy-to-use code for simulating the field scattered by 3D inhomogeneous objects in a stratified medium: tutorial
J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 38, 1841 (2021).
-If the microscopy is used:
S. Khadir, D. Andren, P. C. Chaumet, S. Monneret, N. Bonod, M. Käll, A. Sentenac and G. Baffou
Full optical characterization of single nanoparticles using quantitative phase imaging
Optica 7, 243 (2020). Supplementary Material.
-If the calculation of the optical forces is used, then:
P. C. Chaumet, A. Rahmani, A. Sentenac and G. W. Bryant
Efficient computation of optical forces with the coupled dipole method.
Phys. Rev. E 72, 046708 (2005).
-If the calculation of optical torque is used:
P. C. Chaumet and C. Billaudeau
Coupled dipole method to compute optical torque: Application to a micropropeller.
J. Appl. Phys. 101, 023106 (2007).
-If the rigorous Gaussian beam is used:
P. C. Chaumet
Fully vectorial highly non paraxial beam close to the waist.
J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 23, 3197 (2006).
Contact
email: patrick.chaumet@fresnel.fr, patrick.chaumet@univ-amu.frLicence
Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International (CC BY-NC-SA 4.0)You are free to:
- Share, copy and redistribute the material in any medium or format
- Adapt, remix, transform, and build upon the material
- In addition, you undertake to include citation (see userguide) whenever you present or publish results that are based on it.
- Licensees may copy, distribute, display, and perform the work and make derivative works and remixes based on it only for non-commercial purposes.
- The CNRS makes no warranties of any kind on this software and shall in no event be liable for damages of any kind in connection with the use and exploitation of this technology.
The licensor cannot revoke these freedoms as long as you follow the license terms.