Principal investigator: Guillaume Baffou

Imaging the phase of light, and not only the intensity, is the domain of quantitative phase imaging (QPI) [27]. QPI techniques are conventionally used in microscopy for measuring specific properties of semi-transparent samples without any labelling.
The QPI technique we use is a wavefront imaging technique named Quadriwave Lateral Shearing Interferometry (QLSI) [16,21]. It was invented and patented in 2000 by Jerome Primot (ONERA) [Appl. Optics 39, 5715 (2000)]. It consists of a 2D-grating placed at a millimetric distance from a regular camera. QLSI can reach the diffraction limit, it is achromatic, and thus compatible with the white-light illumination pathway of conventional wide-field microscopes.
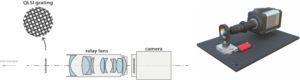
QLSI experimental setup designed at the Fresnel Institute
In 2009, the Institut Fresnel pioneered the use of QLSI for microscopy, a modality that we called cross-grating wavefront microscopy (CGM), and in particular for the observation of living cells in culture [Opt. Express 17, 13080 (2009)]. Since then, our group extended the applications of CGM in nanophotonics in biology. In particular, we demonstrated the ability of CGM to characterize nanoparticles [12,14], 2D-materials [10], metasurfaces [15], microscale temperature profiles [1—9,11,13,17], the growth rate of single bacteria [19], mass transport in neurites of neurons in culture [20]. The figure below illustrate the different objects of interest that have been been investigated by CGM.
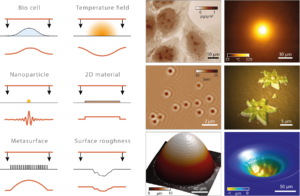
Different objects imaged by CGM at the Fresnel Institute.
We also devote a large part of our activities to numerical simulation, in particular for in-silico experiments of phase microscopy of various kinds [18,26].
We are now actively using QLSI for applications in bio-imaging (neurons, micro-organisms) and nanophotonics (nanoparticles, metasuraces, 2D-materials, biosensing, microfluidics). We usually share all our Matlab codes for data acquisition and processing. In particular, our Matlab toolbox PhaseLAB (~100 000 lignes de code), aimed at processing QLSI images, is available on Github.
CGM image of living cells (U2OS) in culture.
Neurons in culture.
Financial support:
|
|
|
|
References:
2025
- [27] Surface modifications induced by the laser ablation of surface-bound microparticles at low to moderate fluence level in the ultraviolet
Alexandre Beaudier, Baptiste Marthy, Charles Bouyer, Romain Parreault, Guillaume Baffou, Jerome Neauport
Optics Express , accepted (2025)
2024
- [26] Quantitative phase microscopies: accuracy comparison
P. C. Chaumet, P. Bon, G. Maire, A. Sentenac, G. Baffou
Light: Science and Applications 13, 288 (2024)
- [25] Single-shot quantitative phase-fluorescence imaging using cross-grating wavefront microscopy
B. Marthy, M. Bénéfice, G. Baffou
Scientific Report 14, 2142 (2024)
2023
- [24] Quantitative Microscale Thermometry in Droplets Loaded with Gold Nanoparticles
L. Sixdenier,* G. Baffou, C. Tribet, E. Marie
Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters 14, 11200-11207 (2023) - [23] Dry mass photometry of single bacteria using quantitative wavefront microscopy
M. Bénéfice, A. Gorlas, B. Marthy, V. Da Cunha, P. Forterre, A. Sentenac, P. C. Chaumet, G. Baffou*
Biophysical Journal 122, 3159-3172 (2023) - [22] Uniform Huygens Metasurfaces with Postfabrication Phase Pattern Recording Functionality
E. Mikheeva, R. Colom, P. Genevet*, F. Bedu, I. Ozerov, S. Khadir, G. Baffou, R. Abdeddaim, S. Enoch, and J. Lumeau*
ACS Photonics 10, 1538-1546 (2023) - [21] Wavefront microscopy using quadriwave lateral shearing interferometry: from bioimaging to nanophotonics
G. Baffou
ACS Photonics 10, 322-339 (2023)
2022
- [20] Biomass measurements of single neurites in vitro using optical wavefront microscopy
L. Durdevic, A. Resano Gines, A. Roueff, G. Blivet, G. Baffou*
Biomedical Optics Express 13, 6550-6560 (2022) - [19] Life at high temperature observed in vitro upon laser heating of gold nanoparticles
C. Molinaro, M. Bénéfice, A. Gorlas, V. Da Cunha, H. M. L. Robert, R. Catchpole, L. Gallais, P. Forterre, G. Baffou*
Nature Communications 13, 5342 (2022 - [18] Cross-grating phase microscopy (CGM): In-silico experiment (insilex) algorithm, noise and accuracy
B. Marthy, G. Baffou*
Optics Communications 521, 128577 (2022)
2021
- [17] Microscale Thermophoresis in Liquids Induced by Plasmonic Heating and Characterized by Phase and Fluorescence Microscopies
S. Shakib, B. Rogez, S. Khadir, J. Polleux, A. Würger, G. Baffou*
J Phys Chem C 125, 21533-21542 (2021) - [16] Quantitative phase microscopy using quadriwave lateral shearing interferometry (QLSI): principle, terminology, algorithm and grating shadow description
G. Baffou
J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 54, 294002 (2021) - [15] Metasurface optical characterization using quadriwave lateral shearing interferometry
S. Khadir,* D. Andrén, R. Verre, Q. Song, S. Monneret, P. Genevet, M. Käll, G. Baffou*
ACS Photonics 8, 603-613 (2021)
2020
- [14] Full optical characterization of single nanoparticles using quantitative phase imaging
S. Khadir,* Daniel Andrén, P. C. Chaumet, S. Monneret, N. Bonod, M. Käll, A. Sentenac, G. Baffou*
Optica 7, 243-248 (2020)
2019
- [13] Microscale Temperature Shaping Using Spatial Light Modulation on Gold Nanoparticles
L. Durdevic, H. M. L. Robert, B. Wattellier, S. Monneret, G. Baffou*
Scientific Report 9, 4644 (2019) - [12] Quantitative model of the image of a radiating dipole through a microscope
S. Khadir,* P. Chaumet, G. Baffou, A. Sentenac
Journal of the Optical Society of America A 36, 478-484 (2019)
2018
- [11] Photothermal control of heat-shock protein expression at the single cell level
H. M. L. Robert,* J. Savatier, S. Vial, J. Verghese, B. Wattelier, H. Rigneault, S. Monneret, J. Polleux,* and G. Baffou*
Small 14, 1801910 (2018)
2017
- [10] Optical imaging and characterization of graphene and other 2D materials using quantitative phase microscopy
S. Khadir,* P. Bon, D. Vignaud, E. Galopin, N. McEvoy, D. McCloskey, S. Monneret, G. Baffou*
ACS Photonics 4, 3130-3139 (2017)
2016
- [9] Light-Assisted Solvothermal Chemistry Using Plasmonic Nanoparticles
H. M. L. Robert,* F. Kundrat, E. Bermudez-Urena, H. Rigneault, S. Monneret, R. Quidant, J. Polleux, G. Baffou*
ACS Omega 1, 2-8 (2016)
2015
- [8] Quantitative study of the photothermal properties of metallic nanowire networks
A. P. Bell, J. A. Fairfield, E. K. McCarthy, S. Mills, J. J. Boland, G. Baffou, D. McCloskey*
ACS Nano 9, 5551-5558 (2015)
2014
- [7] Deterministic Temperature Shaping using Plasmonic Nanoparticle Assemblies
G. Baffou*, E. Bermúdez Ureña, P. Berto, S. Monneret, R. Quidant and H. Rigneault
Nanoscale 6, 8984-8989 (2014) - [6] Super-Heating and Micro-Bubble Generation around Plasmonic Nanoparticles
under cw Illumination
G. Baffou,* J. Polleux, H. Rigneault, S. Monneret
Journal Physical Chemisty C 118, 4890 (2014)
2013
- [5] Photo-induced heating of nanoparticle arrays
G. Baffou,* P. Berto, E. Bermúdez Ureña, R. Quidant, S. Monneret, J. Polleux, H. Rigneault
ACS Nano 7, 6478-6488 (2013) - [4] Three-dimensional temperature imaging around a gold microwire
P. Bon, N. Belaid, D. Lagrange, C. Bergaud, H. Rigneault, S. Monneret, G. Baffou*
Applied Physics Letters 102, 244103 (2013)
2012
- [3] Quantitative absorption spectroscopy of nano-objects
P. Berto,* E. Bermúdes Ureña, P. Bon, R. Quidant, H. Rigneault, G. Baffou*
Physical Review B 86, 165417 (2012) - [2] Micropatterning Thermoplasmonic Gold Nanoarrays to Manipulate Cell Adhesion
M. Zhu, G. Baffou, N. Meyerbröker, and J. Polleux*
ACS Nano 6, 7227-7233 (2012) - [1] Thermal Imaging of Nanostructures by Quantitative Optical Phase Analysis
G. Baffou,* P. Bon, J. Savatier, J. Polleux, M. Zhu, M. Merlin, H. Rigneault and S. Monneret
ACS Nano 6, 2452-2458 (2012)[1]




