Polarization Microscopy: from single molecules to tissues
Principal investigators : Sophie Brasselet, Miguel Alonso and Luis Aleman-Castaneda
Keywords : polarized fluorescence, polarized super-resolution imaging, polarized nonlinear microscopy
Polarization is an important property of light that is key for how light interacts with matter (for example, reflection, refraction, scattering, fluorescence, etc.). However, polarization is often ignored, in particular for bio-imaging applications. We develop methodologies for optical microscopy that exploit the polarization of light by controling the incident or detected polarization states. These approaches allow retrieving molecular orientational information in biological media, from complex bio-molecular assemblies down to single molecules. The methodology is also applied for the study of nanostructures, either dielectric or metallic.
Excitation fluorescence approaches
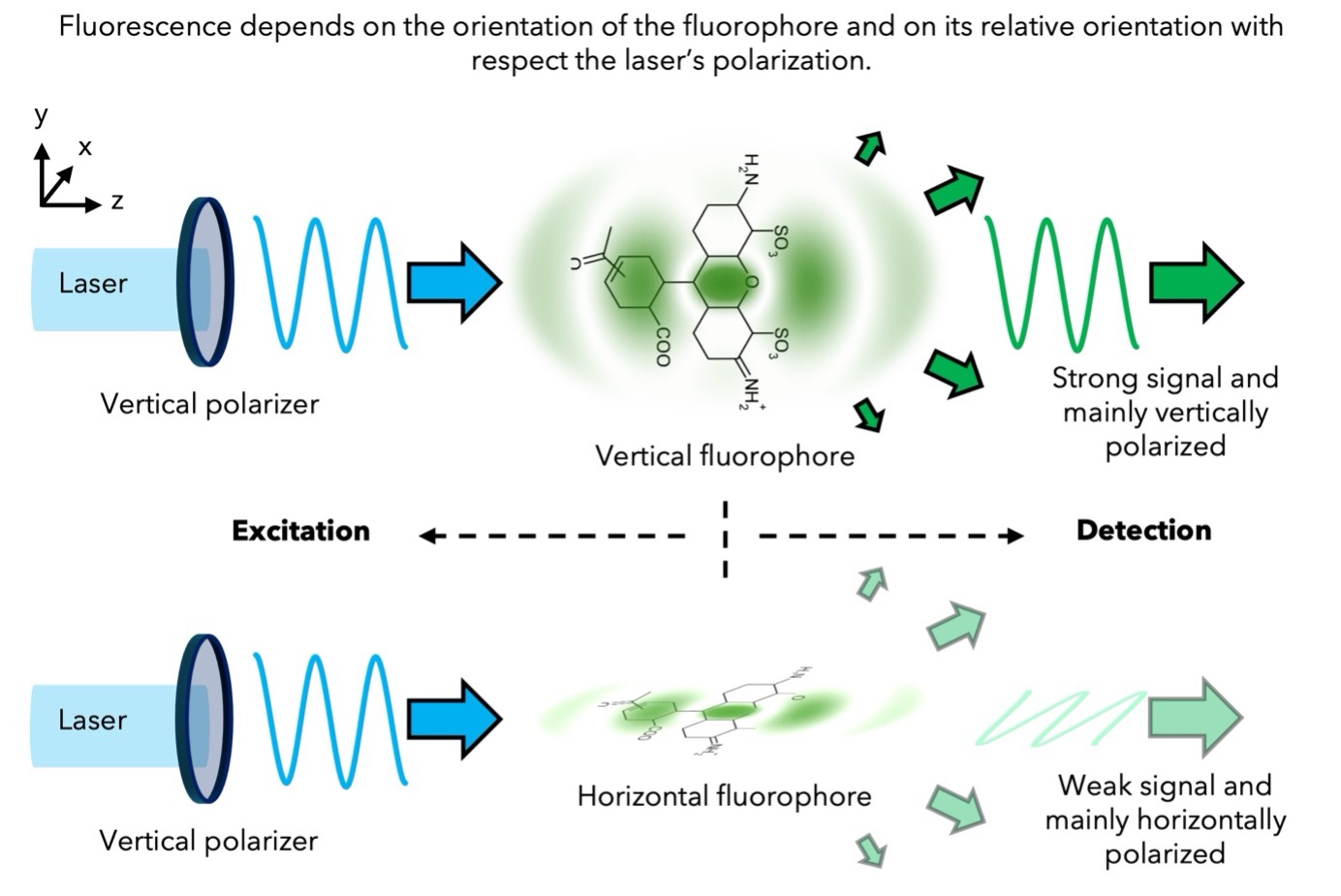
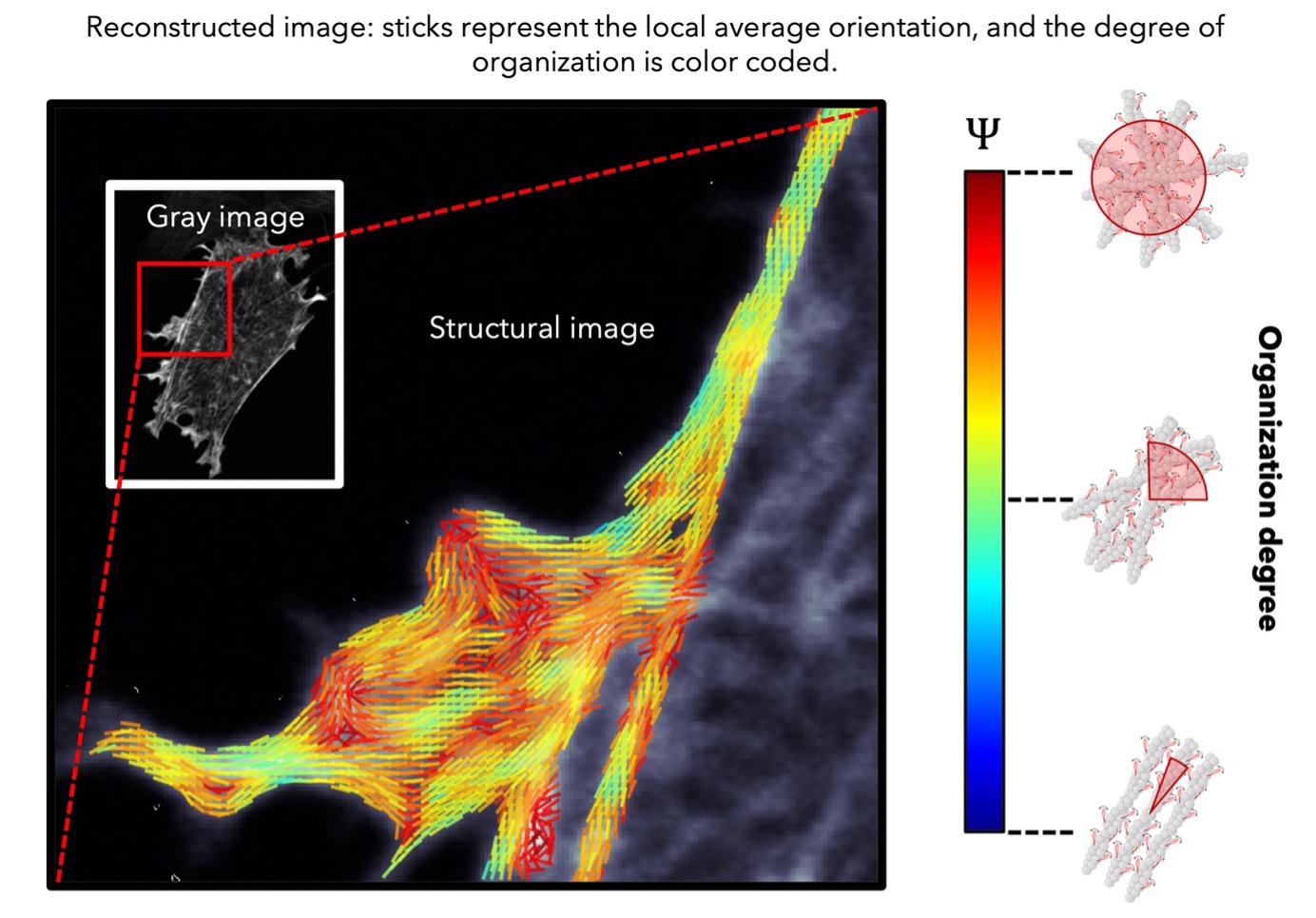
Although these techniques are not compatible with single molecule measurements, they are the most commonly used for bio-molecular assemblies. These techniques exploit the fact that fluorescence is maximized when the polarization state of the excitation laser matches the orientation of molecules. For each pixel of an image, we probe the 2D orientation (projection onto the sample plane) and degree of organization of fluorophores attached to proteins of interest. This approach has been successfully applied to studying the organization of cell membrane lipids and actin filaments, and it can be extended to examine orientational changes in membrane proteins, for example. Additionally, probing molecular organization has great potential for visualizing cytoskeletal filament reorganization, such as during morphogenetic events, in real time at the molecular scale. This can help elucidate how these structures contribute to the mechanical properties of cells and tissues, and reveal the roles of associated regulatory proteins. A major part of this work is currently carried out in collaboration with Manos Mavrakis (MOSAIC team), who studies cytoskeletal proteins such as actin and septin. Lastly, the freely shareable (open source) data analysis software, PyPOLAR, has been co-developed with the Mathematics Institute of Marseille (I2M).
Detection fluorescence approaches
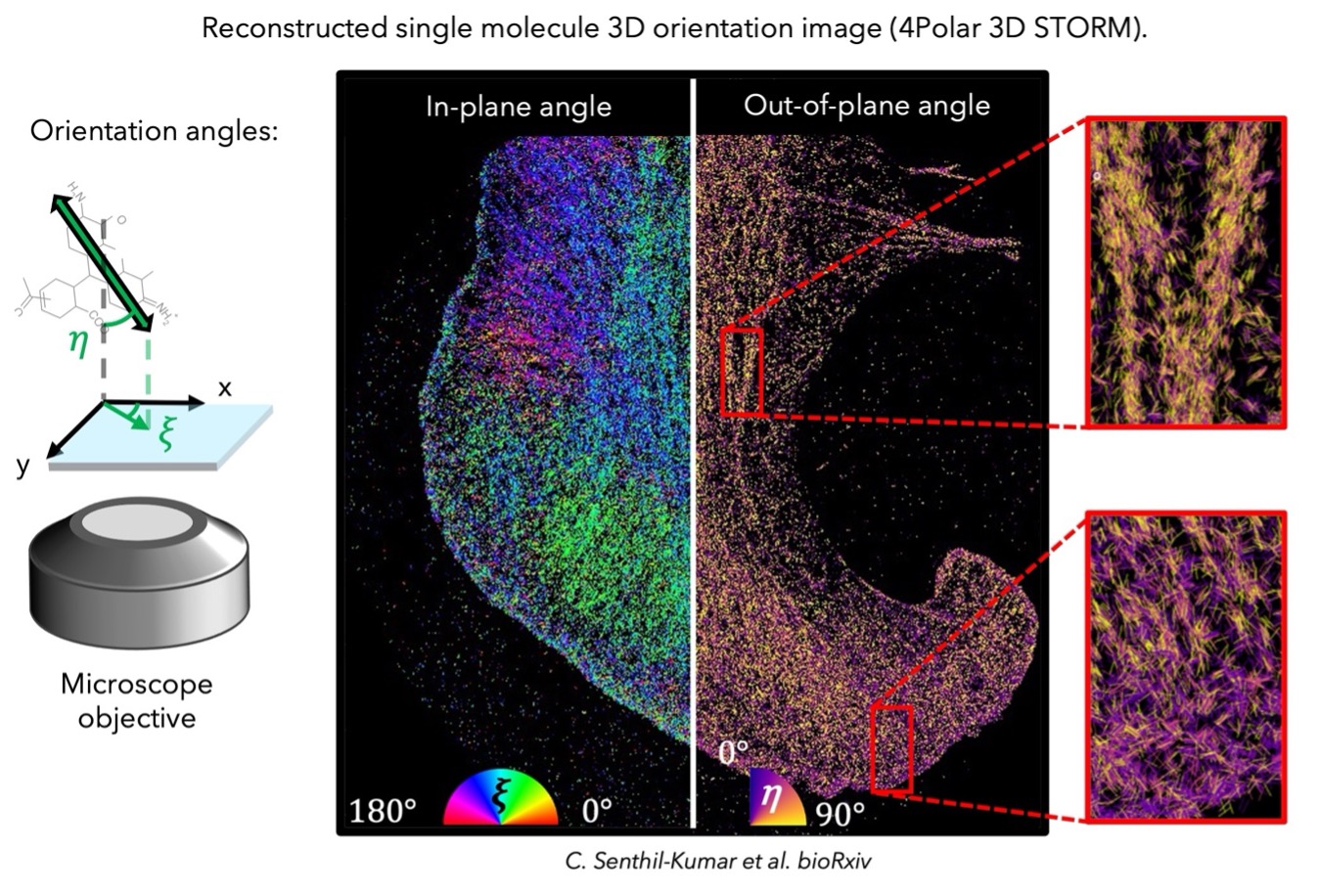
These approaches exploit the distinct fluorescence emission, both in intensity and polarization, that depends on the orientation of each emitter. These approaches can be used with single molecule measurements, meaning that (1) they are compatible with super-resolution imaging (~10 nm by e.g. STORM, PALM, PAINT), and that (2) they can offer information on the mean orientation and wobbling (orientational flexiblitiy) of the single emitters. Note that these techniques can offer easily 3D orientation information compared to the excitation approaches. We have shown the possiblility of reconstructing super-resolution orientation images using their localization information, while the orientational flexibility is an important parameter to quantify that we are able to retrieve realistic structural information on the labeled bio-molecules. This approach has been applied to organized filaments such as dsDNA, actin stress fibers, microtubules. Currently developed and exploited techniques are PSF engineering techniques, such as CHIDO and C3POL, and ratiometric techniques either based on polarization splitting, such as 4Polar and 4Polar 3D, or BFP splitting.
Polarized non-linear imaging
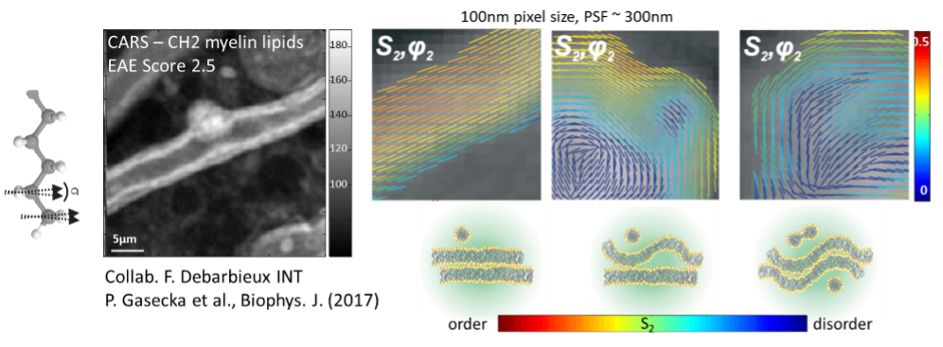
Due to the nonlinear vectorial coupling between incident light polarizations and molecular bonds / molecular induced dipoles directions, tunable incident polarizations lead to a modulation of nonlinear label-free signals (Second Harmonic Generation : SHG, Coherent Anti Stokes Raman Scattering : CARS, Stimulated Raman Scattering : SRS) that can be directly related to the orientational order of biological molecules, without the need of a fluorescent label. We have applied polarized nonlinear microscopy to quantitatively retrieve organizational order in collagen in tissues (by polarized SHG) and lipid structures (by polarized CARS). This methodology is highly sensitive to lipid phases but also to sub-diffraction scale morphological changes in cell membranes. Polarization resolved CARS (pCARS) is now used to image the effect of neurodegenerative diseases on fine myelin structure changes, in mice spinal cord tissues. We are currently developing schemes that allow polarized nonlinear imaging to reach fast imaging rates, either by fast polarization tuning, or via the use of projection on circular polarization combinations. We are also studying the possibilities to develop optical schemes capable to measure the orientation of molecular distributions in 3D, an information which is important in complex tissues. All together these approaches should permit to better quantify molecular order in live and in 3D in tissues related to the study of diseases such as neurodegenerative diseases or cancer.
Theoretical optics of polarization
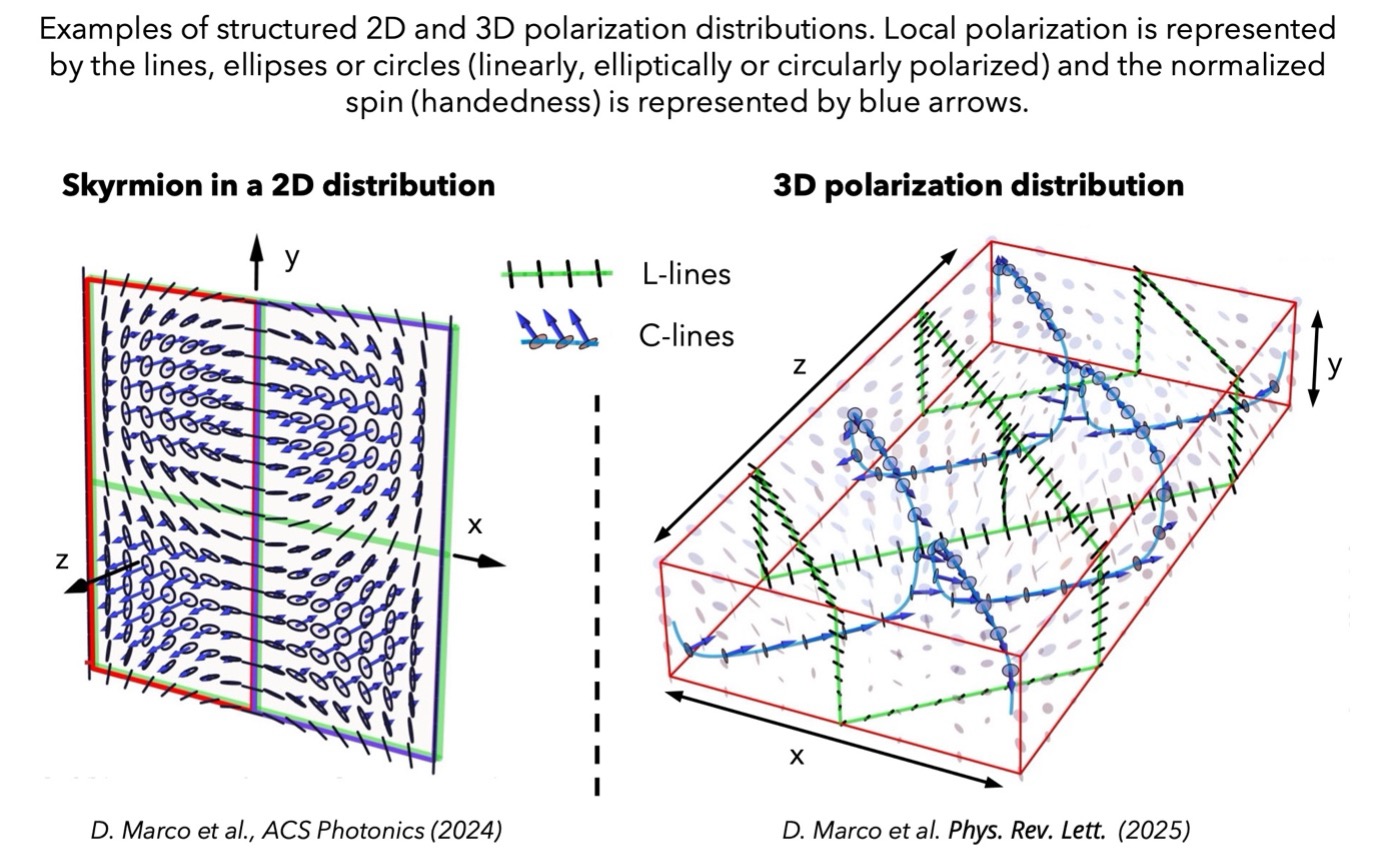
A good theoretical understanding of polarization in the paraxial and nonparaxial regimes is essential for the appropriate estimation and characterization of molecule orientation and wobbling, their effect on the captured images, and the optimization of the imaging systems used to measure them. We study different theoretical formalisms for characterizing the polarization of nonparaxial electromagnetic fields, for which the field oscillations are not constrained to a plane normal to the direction of propagation. We seek for geometric descriptions of these oscillations, valid in different regimes, on the one hand to understand the inherent dimensionality, geometry and topology of these spaces, while on the other to optimize their characterization. We also explore different aspects of nonparaxial polarization of interest beyond fluorescence microscopy, such as the presence of transverse or longitudinal spin, interpretations for geometric phases, or types of electromagnetic field that are analogues of skyrmions.
Developped polarized microscopy techniques
Fluorescence and nonlinear imaging based on excitation schemes:
– Spinning disk fluorescence microscopy (live polarization imaging)
– Nonlinear scanning polarized microscopy (2-photon fluorescence, SHG, CARS, SRS)
Super-resolution and single molecule microscopy based on detection schemes :
– 2D Polarized STORM microscopy
– 3D polarized STORM microscopy (using polarization splitting, BFP splitting or PSF engineering)
Publications
2025
Brasselet S, Lew MD. , Single molecule orientation and localization microscopy, Nat Photonics. 2025 Sep;19:925-937. doi: 10.1038/s41566-025-01724-y
Martins CS, Iv F, Suman SK, Panagiotou TC, Sidor C, Ruso-López M, Plancke CN, Omi S, Pagès R, Gomes M, Llewellyn A, Bandi SR, Ramond L, Arbizzani F, Rimoli CV, Schnorrer F, Robin F, Wilde A, LeGoff L, Pedelacq JD, Jégou A, Cabantous S, Rincon SA, Chandre C, Brasselet S, Mavrakis M. Genetically encoded reporters of actin filament organization in living cells and tissues. Cell. 2025 May 1;188(9):2540-2559.e27. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2025.03.003
2024
Herrera I, Alemán-Castañeda LA, Brasselet S, Alonso MA. Stokes-based analysis for the estimation of 3D dipolar emission. J Opt Soc Am A Opt Image Sci Vis. 2024 Nov 1;41(11):2134-2148. doi:10.1364/JOSAA.538706
R. Gutiérrez-Cuevas, L. Alemán-Castañeda, I. Herrera, S. Brasselet, M. Alonso, Vectorial phase retrieval in super-resolution polarization microscopy. APL Photonics 9, 026106 (2024), doi.org/10.1063/5.0179906
D Marco, I Herrera, S Brasselet, MA Alonso, Propagation-invariant optical meron lattices (2024). arXiv:2402.08650 (2024). ACS Photonics 11(6) pp 2397-2405 (2024). doi.org/10.1021/acsphotonics.4c00292
D. Marco, I. Herrera, S. Brasselet, and M. A. Alonso. Periodic skyrmionic textures via conformal cartographic projections. APL Photonics 9, 110803 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0230959
2023
Martins CS, Taveneau C, Castro-Linares G, Baibakov M, Buzhinsky N, Eroles M, Milanović V, Omi S, Pedelacq JD, Iv F, Bouillard L, Llewellyn A, Gomes M, Belhabib M, Kuzmić M, Verdier-Pinard P, Lee S, Badache A, Kumar S, Chandre C, Brasselet S, Rico F, Rossier O, Koenderink GH, Wenger J, Cabantous S, Mavrakis M. Human septins organize as octamer-based filaments and mediate actin-membrane anchoring in cells. J Cell Biol. 2023 Mar 6;222(3):e202203016. doi: 10.1083/jcb.202203016
Nuzhdin D, Pendleton EG, Munger EB, Mortensen LJ, Brasselet S. In-depth polarisation resolved SHG microscopy in biological tissues using iterative wavefront optimisation. J Microsc. 2023 Jul;291(1):57-72. doi: 10.1111/jmi.13163.
E. Munger, M. Sison and S. Brasselet. Influence of the excitation polarization on single molecule 3D orientation imaging. Opt. Communications (541), 129480 (2023). doi.org/10.1016/j.optcom.2023.129480
S. Brasselet, M.A. Alonso, Polarization microscopy: from ensemble structural imaging to single molecule 3D orientation and localization microscopy. Minireview. Optica 10 (11), 1486-1510 (2023) doi.org/10.1364/OPTICA.502119
2022
Brasselet S. Fluorescence polarization modulation super-resolution imaging provides refined dynamics orientation processes in biological samples. Light Sci Appl. 2022 Nov 7;11(1):322. doi: 10.1038/s41377-022-01018-w.
Brasselet S. Unraveling the geometry of complex protein organizations by polarized fluorescence imaging. Biophys J. 2022 Nov 15;121(22):4242-4243. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2022.09.022.
Alemán-Castañeda LA, Feng SY, Gutiérrez-Cuevas R, Herrera I, Brown TG, Brasselet S, Alonso MA. Using fluorescent beads to emulate single fluorophores. J Opt Soc Am A Opt Image Sci Vis. 2022 Dec 1;39(12):C167-C178. doi: 10.1364/JOSAA.474837
Yang X, Li C, Giorgi M, Siri D, Bugaut X, Chatelet B, Gigmes D, Yemloul M, Hornebecq V, Kermagoret A, Brasselet S, Martinez A, Bardelang D. Energy-Efficient Iodine Uptake by a Molecular Host⋅Guest Crystal. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2022 Dec 5;61(49):e202214039. doi: 10.1002/anie.202214039
Adamczyk AK, Huijben TAPM, Sison M, Di Luca A, Chiarelli G, Vanni S, Brasselet S, Mortensen KI, Stefani FD, Pilo-Pais M, Acuna GP. DNA Self-Assembly of Single Molecules with Deterministic Position and Orientation. ACS Nano. 2022 Oct 25;16(10):16924-16931. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.2c06936.
Arbizzani F, Mavrakis M, Hoya M, Ribas JC, Brasselet S, Paoletti A, Rincon SA. Septin filament compaction into rings requires the anillin Mid2 and contractile ring constriction. Cell Rep. 2022 Apr 19;39(3):110722. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2022.
Rimoli CV, Valades-Cruz CA, Curcio V, Mavrakis M, Brasselet S. 4polar-STORM polarized super-resolution imaging of actin filament organization in cells. Nat Commun. 2022 Jan 13;13(1):301. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-27966-w
2021
J.-Y. Wang, J.C. Mansfield, S. Brasselet, C. Vergari, J.R. Meakin, C.P. Winlove.
Micro-Mechanical Damages of Needle Puncture on Bovine Annulus Fibrosus Fibrils Studies using 1 Polarisation-Resolved Second Harmonic Generation(P-SHG) Microscopy.
Journal of the Mechanical Behavior of Biomedical Materials (2021)
Gasecka P, Balla NK, Sison M, Brasselet S. Lipids-Fluorophores Interactions Probed by Combined Nonlinear Polarized Microscopy. J Phys Chem B. 2021 Dec 23;125(50):13718-13729. doi: 10.1021/acs.jpcb.1c07866.
2020
V. Curcio, L. A. Aleman-Castaneda, T. G. Brown, S. Brasselet, M. A. Alonso,
Birefringent Fourier filtering for single molecule Coordinate and Height super-resolution Imaging with Dithering and Orientation (CHIDO).
Nat. Communications 11 (1) (2020)
DOI : 10.1038/s41467-020-19064-6
2019
N. Mazumder, N K. Balla, G-Y Zhuo, Y V. Kistenev, R Kumar, F-J Kao, S Brasselet, V V. Nikolaev, N A. Krivova.
Label-free Nonlinear Multimodal Optical Microscopy – Basics, Development and Applications,
Frontiers in Physics, Review, 2019
DOI : 10.3389/fphy.2019.00170 (2019)
M.A. Juanes, D. Isnardon, A. Badache, S. Brasselet, M. Mavrakis, B. Goode,
The role of APC-mediated actin assembly in microtubule capture and focal adhesion turnover,
J. Cell Bio. (2019)
DOI : 10.1083/jcb.201904165
J. Rouxel, H. Shen, N. Nguyen, S. Brasselet, T. Toury.
Enhanced second harmonic generation of gold nanostars : optimizing multipolar radiation to improve nonlinear properties,
Opt. Express 27(4), 5620-5640 (2019)
DOI : 10.1364/OE.27.005620
C. Rendon-Barraza, F. Timpu, R. Grange, S. Brasselet.
Crystalline heterogeneity in single ferroelectric nanocrystals revealed by polarized nonlinear microscopy.
Sci. Reports 9, 1670 (2019)
DOI : 10.1038/s41598-018-38229-4
J. Mansfield, V. Mandalia, A. Toms, C. P. Winlove, S. Brasselet.
Collagen reorganization in cartilage under strain probed by polarization sensitive second harmonic generation microscopy
Journal of the Royal Society Interface 16 (150), pp.20180611 (2019)
DOI : 10.1098/rsif.2018.0611
S. Brasselet
Polarized Microscopy in the Life Sciences.
Optics&Photonics News (2019)
2018
N. Chouaki-Benmansour, K. Ruminski, A.-M. Sartre, M.-C. Phelipot, A. Salles, E. Bergot, A. Wu, G. Chicanne, M. Fallet, S. Brustlein, C. Billaudeau, A. Formisano, S. Mailfert, B. Payrastre, D. Marguet, S. Brasselet, Y. Hamon, H.T. He
Phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate regulates the TCR/CD3 complex membrane dynamics and activation,
Sci. Reports 8, 4966 (2018)
doi: org/10.1038/s41598-018-23109-8
N. K. Balla, M. O’Brien, N. McEvoy, G. S. Duesberg, H. Rigneault, S. Brasselet, D. McCloskey.
Effects of Excitonic Resonance on Second and Third Order Nonlinear Scattering from Few-Layer MoS2.
ACS Photonics , 5 (4), pp 1235–1240 (2018)
DOI : 10.1021/acsphotonics.7b00912
O. Loison, M. Weitkunat, A. Kaya-Çopur, C. Nascimento Alves, T. Matzat, M. L. Spletter, S. Luschnig, S. Brasselet, P.-F. Lenne and F. Schnorrer,
Polarization resolved microscopy reveals a muscle myosin motor independent mechanism of molecular actin ordering during sarcomere maturation.
PLoS Biol 16(4) : e2004718 (2018)
DOI : 10.1371/journal.pbio.2004718
2017
H. A. Shaban, C. A. Valades-Cruz, J. Savatier, S. Brasselet,
Polarized super-resolution structural imaging inside amyloid fibrils using Thioflavine T,
Scientific Reports 7 : 12482 (2017)
DOI:10.1038/s41598-017-12864
P. Gasecka, A. Jaouen, F.-Z. Bioud, H. Barbosa de Aguiar, J. Duboisset, P. Ferrand, H. Rigneault, N. Balla, F. Debarbieux, S. Brasselet,
Degradation of molecular organization of myelin lipids in autoimmune demyelination probed by polarization resolved nonlinear vibrational microscopy,
Biophys. J. 113 (7), p1520–1530 (2017).
DOI : 10.1016/j.bpj.2017.07.033
H.B. De Aguiar, S. Gigan, S. Brasselet,
Polarization recovery through scattering media,
Science Advances 3 (9), e1600743 ; (2017),
DOI : 10.1126/sciadv.1600743
C. Cleff, H. Rigneault, S. Brasselet, J. Duboisset,
Nonlinear optical susceptibility described with a spherical formalism, applied to coherent anti-Stokes Raman scattering,
Phys. Rev. A 96, 013851 (2017).
DOI : 10.1103/PhysRevA.94.059902
M. Hofer, N.K. Balla, S. Brasselet,
High speed polarization resolved Coherent Raman Scattering imaging,
Optica 4 (7), pp. 795-801 (2017).
DOI : 10.1364/OPTICA.4.000795.
Highlighted in Biophotonics.World (https://www.biophotonics.world/magazine/article/181/new-imaging-technique-able-to-watch-molecular-dynamics-of-neurodegenerative-diseases) and OSA news release (http://www.osa.org/en-us/about_osa/newsroom/news_releases/2017/new_imaging_technique_fast_enough_to_watch_molecul/)
X. Wang, F. Yang, J. Yin, P. Ferrand, S. Brasselet,
Quantifying the polarization properties of non-depolarizing optical elements with virtual distorting elements,
Applied Optics 56 (10) :2589 (2017)
N.K. Balla, C. Rendon-Barraza, L.M. Hoang, P. Karpinski, E. Bermudez, S. Brasselet,
Polarized nonlinear nanoscopy of metal nanostructures,
ACS Photonics 4 (2), pp 292–301 (2017).
DOI:10.1021/acsphotonics.6b00635
2015
H. B. de Aguiar, P. Gasecka and S. Brasselet
Quantitative analysis of light scattering in polarization-resolved nonlinear microscopy
Opt. Express 23 (7), pp. 8960-8973 (2015)
J. Duboisset, P. Berto, P. Gasecka, F..Z. Bioud, P. Ferrand, H. Rigneault , S. Brasselet
Molecular orientational order probed by coherent anti-Stokes Raman scattering (CARS) and stimulated Raman Scattering (SRS) microscopy : a spectral comparative study
J. Phys. Chem. B 119 (7), pp 3242–3249 (2015)
V. Wasik, P. Réfrégier, M. Roche and S. Brasselet
Precision of polarization-resolved second harmonic generation microscopy limited by photon noise for samples with cylindrical symmetry
JOSA A 32(8) 1437-1445 (2015)
2014
J. Duboisset, H. Rigneault, S. Brasselet
Filtering of matter symmetry properties by circularly polarized nonlinear optics
Phys. Rev. A 90, 063827 (2014)
M. Mavrakis, Y. Azou-Gros, F-C. Tsai, J. Alvarado, A. Bertin, F. Iv, A. Kress, S. Brasselet, G.H. Koenderink and T. Lecuit
Septins promote F-actin ring formation by cross-linking actin filaments into curved bundles
Nature Cell Biology 16, 322–334 (2014)
F.-Z. Bioud, P. Gasecka, P. Ferrand, H. Rigneault, J. Duboisset, and S. Brasselet
Structure of molecular packing probed by polarization-resolved nonlinear four-wave mixing and coherent anti-Stokes Raman scattering microscopy
Phys. Rev. A 89, 013836 (2014)
P. Ferrand, P. Gasecka, A. Kress, X. Wang, F.-Z. Bioud, J. Duboisset, S. Brasselet
Ultimate use of two-photon fluorescence microscopy to map fluorophores orientational behavior
Biophys. J. 106 2330–2339 (2014)
2013
A. Kress, X. Wang, H. Ranchon, J. Savatier, H. Rigneault, P. Ferrand, S. Brasselet
Mapping the local organization of cell membranes using generalized polarization resolved confocal fluorescence microscopy
Biophys. J. 105, 127-136 (2013)
H. Shen, N. Nguyen, D. Gachet, V. Maillard, T. Toury, S. Brasselet
Nanoscale optical properties of metal nanoparticles probed by Second Harmonic Generation microscopy
Opt. Express 21 (10), pp.12318-12326 (2013)
X. Wang, A. Kress, S. Brasselet, P. Ferrand
High frame-rate confocal angular resolved linear dichroism fluorescence microscopy
Rev. Sc. Instr. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 84, 053708 (2013)
J. Duboisset, P. Ferrand, H. Wei, X. Wang, H. Rigneault, S. Brasselet
Thioflavine-T and Congo Red Reveal the Polymorphism of Insulin Amyloid Fibrils when Probed by Polarization-Resolved Fluorescence Microscopy
J. Phys. Chem. B, 2013, 117 (3), pp 784–788
2012
S. Brasselet, P. Ferrand, A. Kress, X. Wang, H. Ranchon, A. Gasecka
Imaging Molecular Order in Cell Membranes by Polarization-Resolved Fluorescence Microscopy
Y. Mély and G. Duportail (eds.), Fluorescent Methods to Study Biological Membranes, Springer Series Fluorescence
Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg 2012, 13, 311-338 (2013)
P. Refregier, M. Roche, J. Duboisset, S. Brasselet
Precision increase with two orthogonal analyzers in polarization resolved second harmonic generation microscopy
Opt. Lett. 37 (20), pp.4173-4175 (2012)
D. Ait-Belkacem, M. Guilbert, M. Roche, J. Duboisset, P. Ferrand, G. Sockalingum, P. Jeannesson, and S. Brasselet
Microscopic structural study of collagen aging in isolated fibrils using polarized second harmonic generation
J. Biomed. Opt. 17, 080506 (2012)
F. Munhoz, H. Rigneault, S. Brasselet
Polarization–resolved four-wave mixing for structural imaging in thick tissues
J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 29 (6), pp.1541-1550 (2012)
J. Duboisset, Dora Aït-Belkacem, Muriel Roche, Hervé Rigneault, Sophie Brasselet
Generic model of the molecular orientational distribution probed by polarization resolved Second Harmonic Generation
Phys. Rev. A. 85, 043829-38 (2012)
A. Gasecka, P. Tauc, A. Bentley, S. Brasselet
Investigation of Molecular and Protein Crystals by Three Photon Polarization Resolved Microscopy
Phys Rev Lett 108, 263901-05 (2012)
F. Munhoz, S. Brustlein, R. Hostein, P. Berto, S. Brasselet and H. Rigneault
Polarization resolved stimulated Raman scattering : probing depolarization ratios of liquids
Journal of Raman Spectroscopy 43 (3), 419–424 (2012)
S. Monneret, S. Brasselet
Advanced microscopy techniques for biological imaging
Int. J. Nanotechnol., Vol. 9 (3–7), 548-566 (2012)
2011
A. Kress, P. Ferrand, H. Rigneault, T. Trombik, H.-T. He, D. Marguet, S. Brasselet
Probing orientational behavior of MHC Class I protein and lipid probes in cell membranes by fluorescence polarization-resolved imaging
Biophys. J. 101, pp. 468–476 (2011)
P. Refregier, M. Roche, S. Brasselet
Precision analysis in polarization-resolved second harmonic generation microscopy
Opt. Lett. Vol. 36 (11), pp. 2149-2151 (2011)
S. Brasselet
Polarization resolved nonlinear microscopy : application to structural molecular and biological imaging
Advances in Optics and Photonics 3, pp. 205–271 (2011)
2010
F. Munhoz, H. Rigneault, S. Brasselet
High Order Symmetry Structural Properties of Vibrational Resonances Using Multiple-Field Polarization Coherent Anti-Stokes Raman Spectroscopy Microscopy
Phys Rev Lett. 105, 123903 (2010)
D. Aït-Belkacem, A. Gasecka, F. Munhoz, S. Brustlein, and S. Brasselet
Influence of birefringence on polarization resolved nonlinear microscopy and collagen SHG structural imaging
Opt. Express 18 (14) 14859-14870 (2010)
S. Brasselet
Second Harmonic Generation microscopy in molecular crystalline nano-objects
Nonlinear Optics, Quantum Optics NLOQO, 40 (1-4), pp 83-94 (2010)
A. Gasecka, L-Q. Dieu, D. Bruehviler, S. Brasselet
Probing molecular order in zeolite L inclusion compounds using two-photon fluorescence polarimetric microscopy
J. Phys. Chem. B 114 (12), pp 4192–4198 (2010)
P. Schön, M. Behrndt, D. Ait-Belkacem, H. Rigneault, S. Brasselet
Polarization and Phase Pulse Shaping applied to Structural Contrast in Nonlinear Microscopy Imaging
Phys. Rev. A 81, 013809 (2010)
2009
F. Munhoz, S. Brustlein, D. Gachet, F. Billard, S. Brasselet, H. Rigneault
Raman depolarization ratio of liquids probed by linear polarization Coherent Anti-Stokes Raman spectroscopy
Journal of Raman Spectroscopy, vol. 40, (7), 775-780 (2009)
A. Gasecka, T.-J. Han, C. Favard, B.R. Cho, S. Brasselet
Quantitative imaging of molecular order in lipid membranes using two-photon fuorescence polarimetry
Biophys J. 97 (10) 2854-2862 (2009)

