Overview
This home made-program
uses a global optimization procedure developed by T. Csendes et Al. in
respiratory system modelling.
The multi-dimensional space composed of the different parameters (thickness)
is divided into clusters formed by single linkage method.
The distance between a set of initial parameters X0 and the parameters
X10 corresponding to the local minimum found is evaluated. A new point
X1 will join the (X0; X10) cluster if there is a point in the cluster
with which the distance is less than a critical distance calculated automatically
by the program. If the new point is not clustered, a new local minimum
X11 is searched.
The process is repeated until the whole space, possibly reduced to a nominal
interval is clustered. The local search procedure is an algorithm of Quasi-Newton
type which uses the Davidon-Fletcher-Powell formula.
T. Csendes, B. Daroczy, Z. Hanos, “Nonlinear parameter estimation
by global optimization: comparison of local search methods in respiratory
system modelling”, System Modelling and Optimization, 188-192, Springer
Verlag, Berlin, 1986
Results
Optical Interference Coatings 2004 (Tucson): 2nd place (Design Problem A) and winner of the Design Problem B. Click here for more information.
Needle optimization technique with Quasi-Newton
algorithm:
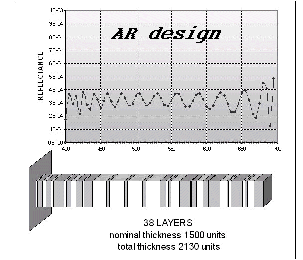
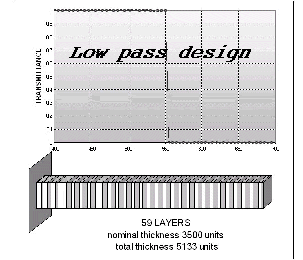
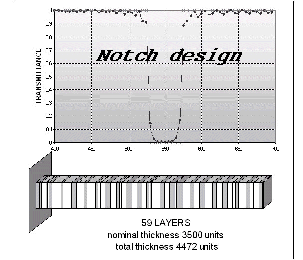
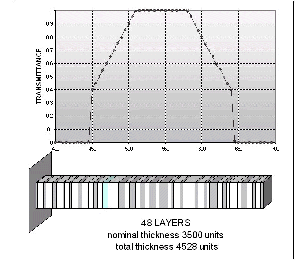
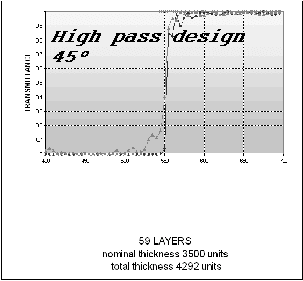
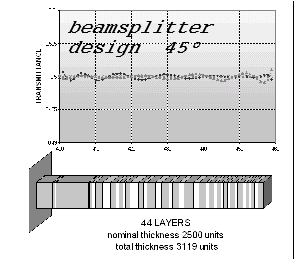
Examples of Optical Coating Designs
Starting Design
One single high index layer.
The nominal thickness influences the number of layers of the final solution.
Data
Glass Refractive index ns
= 1.52
Supertrate medium Air n = 1.
High index material: nh = 2.35
Low index material: nb = 1.45
Cross points: target
Diamond-shaped points: spectral response of the optimized coating
Normal Incidence
45 degree incidence
Light gray points: p-polarisation
Dark grey points: s-polarisation